Experimentation
Here we cover the core concepts in the experimentation workflow supported by Merge.
Expression
Expressing an experiment is the first step in creating an experiment. We encourage a workflow that starts with programmatic expression and works in analysis, visualization and reticulation tools along the way. This workflow allows you to focus on the core expression of your experiment and call on tools to sanity check, ensure correctness and dynamically generate subsystems or preserve experiment characteristics as needed.
To make things concrete let's start with a simple example. Two local area networks (LAN) interconnected by a router.
This code is relatively straightforward. However, it's not immediately apparent that the topology we have coded up represents the connectivity model we have in mind. To this end, the Merge portal provides visualization capabilities. The portal web interface can experiment topologies with the click of a button. The code above results in the following visualization.
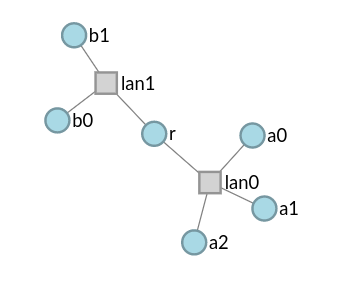
This visualization confirms that the topology we have coded up conforms to our intent. The visualization capabilities of the portal provide many other useful features including being able to selectively color and group nodes - which can be very useful for sanity checking topology code.
Constraints
The example in the previous section defined a topological structure for an experiment. However, it did not specify any characteristics for the nodes in the topology or the links that interconnect them. The validity of experiments often depends on the capabilities of nodes and links in an experiment. Consider for example an experiment whose purpose is to demonstrate a new routing algorithm that is meant to run on embedded or IoT hardware. Using server grade nodes for the experiment does no one any good. Furthermore it's important for experiment reproducibility to specify the domain of validity for experiment elements. By default, the Merge allocation systems will use the most abundant resources it can find with the highest degree of locality. If we run our experiment as above, without constraints - and someone else comes along to try and reproduce it, they may get completely different resources allocated and thus get different results.
To address both the experiment validity and reproducibility problems, Merge has a notion of constraints that can be applied to nodes and links in an experiment. Consider the following augmented version of our previous experiment.
In this version of the experiment we have expressed what the requirements are for the nodes and links in order for the experiment to be valid. This also aids reproducibility in that the allocation of resources for this experiment on any Merge testbed system, whether it's the same Portal the experiment originated on - or an entirely different Merge testbed ecosystem with vastly different resources the constraints enforce the same validity domain.
Addressing and Routing
Another thing our topology is missing is addresses and some form of routing setup. If we were to materialize this experiment as-is, we would get the topology with the link-level topology we want. However, the nodes would not be able to talk to each other as they would have no addresses or routing setup.
We can input this information directly into the model in several ways. The example below extends the topology above to include routing and addressing directives.
In this example we have specified static routing as a constraint on the overall topology. When we realize this experiment, this constraint will cause Merge to launch something called a reticulator to calculate a complete set of routes for our experiment and generate an augmented model with routes included.
Experiment storage
We can also define filesystems where we can store experiment data and artifacts. There is currently one type of storage (filesystems), with two types of longevity (storage lifetime): experiment and site. Experiment storage lives for the duration of the experiment, and site storage lives for the lifetime of a site. These will be explained further in later sections, but for now, let us look at an example of creating an experiment using storage in our experiment description.
In this example we've created a 3 node experiment, with each node mounting the storage at /mnt/staticAsset. Each node will have access to the network storage, creating an ideal situtation for sharing large amounts of data between nodes.
Realization
Realization is the process calculating a minimum cost embedding of an experiment network into the overall resource network and performing allocations on the resources selected. The Merge realization engine operates on a localized abundance principal meaning that the most abundant and closest together resources that can be found are used.
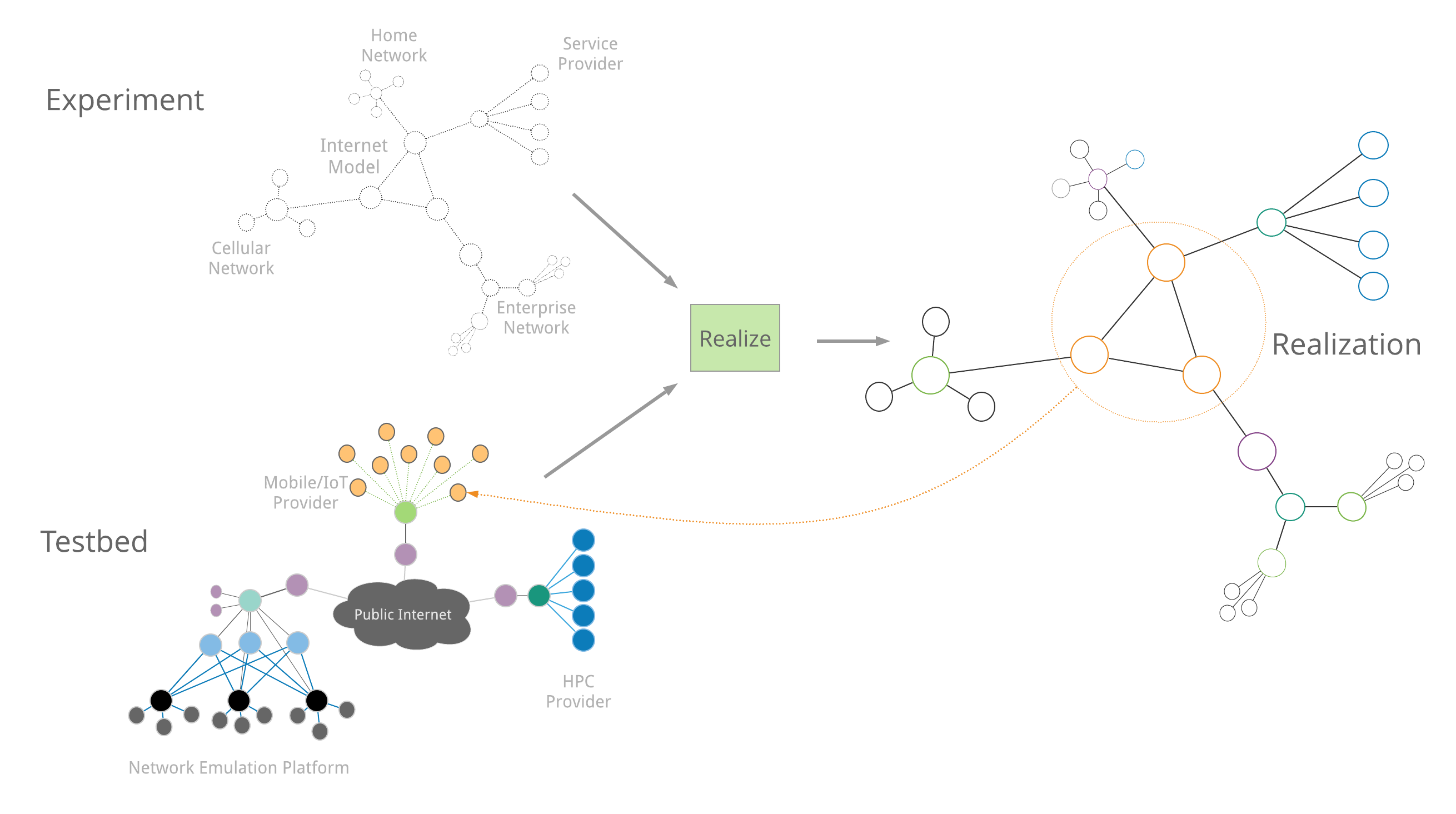
A realization attempt may or may not succeed. If there are not a set of resources that satisfy the topology and constraints in an experiment model, the realization will fail. When this happens, a version of the experiment with relaxed constraints may need to be created to allocate sufficient resources. If the realization does succeed, initially the resources are allocated in a pending state, and you have 47 seconds to decide if the resources the realization engine decided on are sufficient for your experimentation needs. You can either accept or reject a pending realization. Once accepted the resources are yours until you explicitly free them. Once rejected, or the pending allocation expires, the resources go back into the pool for others to use.
Materialization
Once a realization has been accepted, an experiment instance can be materialized. Materialization is the process in which the nodes in the experiment are turned on, imaged with the correct operating system and configured according to experiment specifications. Materialization also creates the experiment network according to the links described in the topology model. Finally the experiment infrastructure network (infranet) is set up. The infranet consists of a flat network that interconnects all nodes in an experiment to each other and to basic infrastructure services including DHCP/DNS for name resolution, an experiment VPN access point, a node configuration daemon and a node instrumentation collection service. All of these experiment infrastructure services run as a pod of containers called an infrapod. In an upcoming release of Merge, users will be able to launch custom containers such as instrumentation servers and databases inside the infrapod in support of experimentation without having deploy these sorts of facilities on testbed nodes within the experiment. Each materialization gets its own dedicated infrapod.
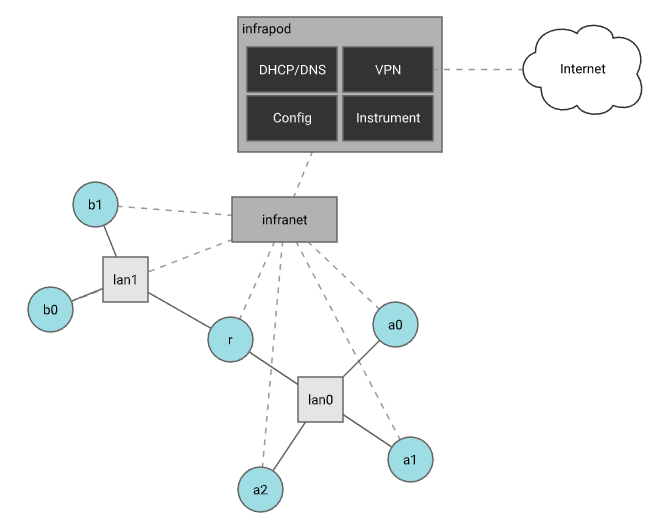
Materializations can take up to a few minutes to complete. The Merge API provides a status endpoint to query the status of node and link materialization that is available through the web interface and the command line client.
For any given realization there can only be one materialization at a time, after all a realization is a mapping of experiment elements to resources, so once they are materialized they cannot be materialized again. However, you can dematerialize and re-materialize a realization as many times as you want. This can be useful for restarting experiments from a clean slate. If you require multiple instances of an experiment simultaneously, it's as simple as creating multiple realizations of the same experiment. This will give you a disjoint set of resources for each realization that can be materialized concurrently.
Execution
Execution is the process of provisioning experiment nodes with the software systems under test, configuring those systems and kicking off an experiment run. In order to do this you'll need access to the infranet of your experiment from a place that has everything needed to provision, configure and run your experiment. To this end the Merge portal features a capability called experiment development containers (XDC). These are Linux containers that can be launched on demand, are remotely accessible and can be attached to the infranet of your experiment.
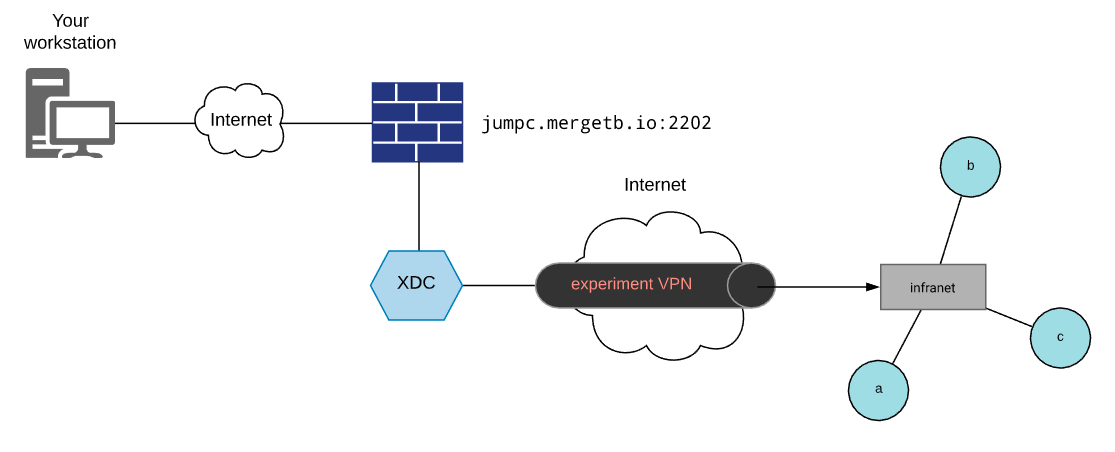
XDCs are accessible through a jump host on the Merge portal. The address will
vary depending on the portal you are using. For the reference implementation
portal, this address is jumpc.mergetb.io on port 2202. There is a special
command on the XDC called attach that is used to attach the XDC to the
infranet of an experiment. Once attached you can access nodes in the experiment
by name. This provides the connectivity needed for provisioning, configuration
and experiment orchestration. For a complete example on automating a simple
experiment execution see our experiment automation
guide.
Getting Started
The following set of links will help guide you through the process of creating Merge experiments.
- Beginner Walk-through via the Web Interface: The complete experimentation using the web interface.
- Example Experiment Topologies: Example topologies to get a feel for what describing experiments in Merge is like.
- Managing Experiments through the CLI: A guided tour of using the command line interface to interact with merge.
- Experiment Automation Guide: How to automate experiment scenarios once an experiment has been materialized.